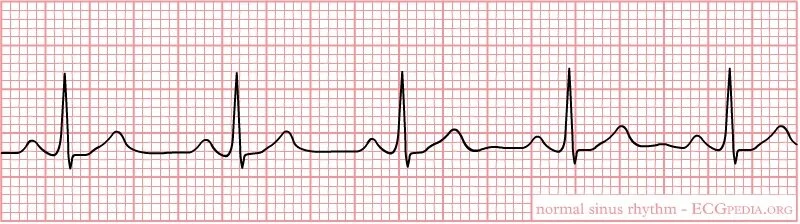
RHYTHM Assessment
One of the first things you assess in the ICU patient is the cardiac rhythm. Cardiac rhythms will impact the hemodynamic stability of the patient.
Anything other than normal sinus rhythm is abnormal!
It’s very important to be able to assess rhythms. You should practice identifying rhythms until you become confident in their identification.
Below are some simple ways to learn to identify cardiac rhythms.
Ask these questions every time:
What is the rate?
Atrial rate?
Ventricular rate?
Is the rhythm regular?
Is every P wave followed by a QRS?
Are The intervals within normal range?
Know the normal interval values:
PRI = 0.12 to 0.20
QRS = 0.06 to 0.12
NSR: rate 60-100 normal PRI
ST: rate >100, normal PRI
SB: rate <60, normal PRI
(PRI= PR interval, NSR= Normal sinus rhythm, ST= Sinus tachycardia, SB= Sinus bradycardia)
❇️ Here are the steps to rhythm assessment:
◼️Determine the atrial and ventricular regularity:
♦️Is the P-P interval consistent?
♦️Is the R-R interval consistent?
◼️ Determine the atrial and ventricular rates:
♦️ Are they the same?
♦️Is the rate > 100 beats/min? (tachycardia)
♦️Is the rate < 60 beats/min? (bradycardia)
◼️ Identify P waves
♦️ Are P waves present? If not,what atrial activity is seen?
♦️Do the P waves all look the same?
♦️Is every P wave followed by a QRS complex?
◼️ Measure the P-R interval
♦️ Is the P-R interval within normal limits (0.12-0.20 sec)?
♦️Is the P-R interval the same for each ECG complex?
◼️ Identify the QRS complex
♦️ Are QRS complexes present?
♦️Do the QRS complexes all look the same?
♦️Is there 1 and only 1 P wave before each QRS complex?
◼️ Measure the QRS interval
♦️Is the QRS interval within normal limits(0.04-0.10sec)?
♦️Is the QRS interval the same for every ECG complex?
⚠️All abnormal rhythm changes should be promptly reported to the provider... even if they last for 3 seconds/transient/self-resolving.
⚠️Abnormal rhythms can cause significant changes in hemodynamics and death.
Become familiar with the most common arrhythmias/dysrhythmias:
Premature Atrial Contractions (PAC’s):
Premature beats will have a P wave that may look different than the normal P-wave
QRS <0.12
Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVC’s):
Premature beats have no P waves in front of them
The QRS complex will be wide and bizarre and measure >0.12
No PRI
Atrial Tachycardia:
HR 150 - 250 bpm
Rhythm is usually regular (R - R intervals are equal)
P waves proceed QRS (May be difficult to see due to the rate)
PRI and QRS are within normal limits
Atrial Fibrillation:
Can’t measure atrial rate, the ventricular rate usually less than 100 bpm
Rhythm is generally irregular
No distinguishable P waves
QRS is within normal limits
Atrial Flutter:
HR 250 - 350 bpm
Rhythm is usually regular with rapid atrial rate
P waves take on a sawtooth look called flutter waves
PRI cannot be determined
QRS is within normal limits
Ventricular Tachycardia (VT):
HR 150 - 250 bpm
Rhythm is usually regular with a fast ventricular rate
No P waves
QRS is wide and bizarre and measures > 0.12
Ventricular Fibrillation (VF):
HR can’t be determined
Chaotic appearance of the rhythm
No waveforms can be identified
Below is an extensive list of Dysrhythmias:
- sinus bradycardia
- sinus tachycardia
- sinus arrhythmia
- sinus block
- sinus arrest
- premature atrial contraction
- atrial tachycardia
- multifocal atrial tachycardia
- atrial flutter
- atrial fibrillation
- proximal atrial tachycardia
- premature junctional contraction
- junctional rhythm
- accelerated junctional rhythm
- junctional tachycardia
- first-degree AV block
- second-degree AV block Mobitz I
-second-degree AV block Mobitz II
-AV block
- left bundle branch block
- right bundle branch block
- premature ventricular contraction
- ventricular tachycardia
- Torsades de pointes
- ventricular flutter
- ventricular fibrillation
- asystole
Learn more about rhythm interpretation here!
Download an ECG reference card here!